By Yo-Han Kim, Rie Nagata, Natsuki Ohtani, Toshihiro Ichijo, Kentaro Ikuta, and Shigeru Sato
This study demonstrated that feeding dietary forage alleviates subacute ruminal acidosis due to diurnal changes in ruminal pH.
Read
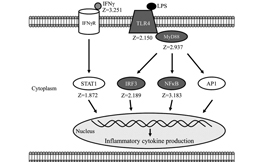
By Yo-Han KIM, Noriyuki TOJI, Keiichiro KIZAKI, Kei TAKEMURA, Shiro KUSHIBIKI, Shigeru SATO
In this 2019 paper published in The Journal of Veterinary Medical Science, the authors found feeding the only starter to calves decreases rumen pH at weaning with upregulation of the receptor TLR4. Feeding only starter lowered cholesterol synthesis in the rumen epithelium whereas starter and forage combined resulted in higher energy status.
Read
By J H McCaughern, A M Mackenzie, L A Sinclair
The results of a study in 60 Holstein-Friesian dairy cows highlight the need to take account of dietary effects on rumen pH when deciding on appropriate copper supplementation levels.
Read
By Jörg R. Aschenbach, Qendrim Zebeli, Amlan K. Patra, Gabriele Greco, Salah Amasheh, Gregory B. Penner
The ruminal epithelium is the main site for absorption of key nutrients and electrolytes. Yet, the absorptive function has to be highly selective to prevent entry of microbes and toxins. This study outlines what researchers know, and still must uncover, about the factors that counteract barrier impairment and help with barrier restoration.
Read
By Robin R. White, Mary Beth Hall, Jeffrey L. Firkins, Paul J. Kononoff
This study by U.S. researchers quantifies the links between neutral detergent fiber (NDF) intake, diet particle size and ruminal pH.
Read
Download the final report of The first international conference dedicated to acidosis and rumen health, including video recordings.
Read
By Meissner. S, Hagen. F, Deiner. C, Günzel. D, Greco. G, Shen. Z, Aschenbach. JR
Sub Acute Ruminal Acidosis (SARA) is induced by high concentrations of short-chain fatty acids (SCFA) that result in lower ruminal pH and damage to the epithelial barrier function. The present study investigated if SCFA directly contribute to epithelial barrier failure.
Read
By Villot C, Meunier B, Bodin J, Martin C, Silberberg M
Sub Acute Ruminal Acidosis (SARA) is defined as a drop in rumen pH, but what is the most accurate way to look at these pH variations? This study addressed this important research question and even accounted for individual variabilities.
Read
By P. Pourazad, R. Khiaosa-ard, M. Qumar, S. U. Wetzels, F. Klevenhusen, B. U. Metzler-Zebeli, Q. Zebeli
Rumen health is affected by what is fed — and also how its fed. This study shows the relationship between patterns of concentrate-rich feeding and the severity of Sub Acute Ruminal Acidosis (SARA) and rumen VFAs profiles.
Read
By Jan C. Plaizier, Shucong Li, Anne Mette Danscher, Hooman Derakshani, Pia H. Andersen, Ehsan Khafipour
A study showing how a grain-based diet-induced subacute ruminal acidosis (SARA) challenge impacts the rumen microbiota of lactating dairy cows. The richness, the diversity, as well as the stability of the bacterial communities were reduced for SARA challenged cows. Both ruminal and fecal microbiota were changed, indicating that the rumen but also the hindgut microbiota are affected by SARA challenge.
Read