Rumen Health Technical Guide
Leading ruminant experts have written the Rumen Health Technical Guide. This resource is free to veterinarians, nutritionists and producers, request a copy today.
 Get a copy
Get a copy
Laminitis
Inflammatory status of the hoof wall, is due to histamineGlossaryView allHistamine
Vasomotor amine released by bacteria activity during a decrease in ruminal pH. Histamine has an effect on blood vessels causing an inflammation that can weaken the laminar structure in the hoof wall. produced by some rumen bacteria under low pH.
- The etiology of laminitis is multi-faceted, but is generally the result of prolonged exposure to low rumen pH that is caused by nutritional factors that lead to acidosis.12ReferenceView allNocek J. E. 1997.
36ReferenceView allLean I.J., Westwood C.T., Golder H.M., Vermunt J.J. 2013.
37ReferenceView allHuxley J.N. 2013.
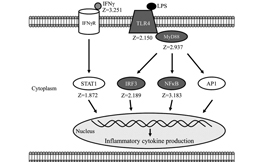
- The initial activation of laminitis starts with the low rumen pH, lysis or death of gram-negative bacteria lead to the release of lipopolysaccharideGlossaryView allLipopolysaccharide
Essential component of the cell wall of negative gram bacteria. This molecule is released in the bloodstream can induce inflammatory responses. (LPS), a cell wall component which is a very potent stimulator of inflammation.
- HistamineGlossaryView allHistamine
Vasomotor amine released by bacteria activity during a decrease in ruminal pH. Histamine has an effect on blood vessels causing an inflammation that can weaken the laminar structure in the hoof wall. is also produced by some rumen bacteria under low pH, and by an animal under stress. Histamine is also an inflammatory compound. Due to repeated acid insults on the rumen and the hindgut wall, the epithelial barrier is disrupted and these inflammatory molecules can be transferred to the bloodstream.
- Histamine production leads to an inflammatory condition in the animal that can weaken the laminar structure in the hoof wall, thus leading to laminitis.